French language
Definition
| French | |
|---|---|
| français | |
| Pronunciation | [fʁɑ̃sɛ] |
| Native to | France |
| Region | Francophonie (French-speaking world) (geographical distribution below) |
Native speakers | 79 million speakers worldwide (2012) An estimated 274 million French speakers (L1 plus L2; 2014) |
Language family | Indo-European
|
Early forms | Old French
|
| Dialects |
|
Writing system | Latin (French alphabet) French Braille |
Signed forms | Signed French (français signé) |
| Official status | |
Official language in | Numerous international organisations |
| Regulated by | Académie française(French Academy) (France) Office québécois de la langue française(Quebec Board of the French Language) (Quebec) |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | fr |
| ISO 639-2 | fre (B)fra (T) |
| ISO 639-3 | fra |
| Glottolog | stan1290 |
| Linguasphere | 51-AAA-i |
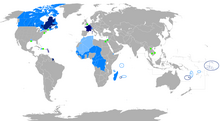 Regions where French is a majority native language Regions where it is an official language but not a majority native language Regions where it is a second language Regions where it is a minority language | |
French is an official language in 29 countries across five different continents, most of which are members of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie (OIF), the community of 84 countries which share the official use or teaching of French. It is spoken as a first language (in descending order of the number of speakers) in France, Canadian provinces of Quebec, Ontario and New Brunswick as well as other Francophone regions, Belgium (Wallonia and Brussels), western Switzerland (cantons of Bern, Fribourg, Geneva, Jura, Neuchâtel, Vaud, Valais), Monaco, parts of the United States (Louisiana, Maine, New Hampshire, and Vermont), and by various communities elsewhere. In 2015, approximately 40% of the francophone population (including L2 and partial speakers) lived in Europe, 35% in sub-Saharan Africa, 15% in North Africa and the Middle East, 8% in the Americas, and 1% in Asia and Oceania. French is the fourth most widely spoken mother tongue in the European Union, Of Europeans who speak other languages natively, approximately one-fifth are able to speak French as a second language. French is the second most taught foreign language in the EU. French is also the 18th most natively spoken language in the world, and is the second most studied language worldwide (with about 120 million current learners).
As a result of French and Belgian colonialism from the 16th century onward, French was introduced to new territories in the Americas, Africa and Asia. Most second-language speakers reside in Francophone Africa, in particular Gabon, Algeria, Mauritius, Senegal and Ivory Coast.
French is estimated to have about 76 million native speakers, and another 77 to 110 million secondary speakers who speak it as a second language to varying degrees of proficiency, mainly in Africa. According to the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie (OIF), approximately 274 million people worldwide are "able to speak the language", without specifying the criteria for this estimation or whom it encompasses.According to a demographic projection led by the Université Laval and the Réseau Démographie de l'Agence universitaire de la francophonie, the total number of French speakers will reach approximately 500 million in 2025 and 650 million by 2050. OIF estimates 700 million by 2050, 80% of whom will be in Africa.
French has a long history as an international language of literature and scientific standards and is a primary or second language of many international organisations including the United Nations, the European Union, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, the World Trade Organization, the International Olympic Committee, and the International Committee of the Red Cross. In 2011, Bloomberg Businessweek ranked French the third most useful language for business, after English and Standard Mandarin Chinese.
Geographic distribution
Europe
Spoken by 12% of the European Union's population, French is the fourth most widely spoken mother tongue in the EU after German, English and Italian; it is also the third-most widely known language of the Union after English and German (33% of the EU population report knowing how to speak English, 22% of Europeans understand German, 20% French).
Under the Constitution of France, French has been the official language of the Republic since 1992(although the ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts made it mandatory for legal documents in 1539). France mandates the use of French in official government publications, public education except in specific cases (though these dispositions are often ignored) and legal contracts; advertisements must bear a translation of foreign words.
In Belgium, French is the official language of Wallonia (excluding a part of the East Cantons, which are German-speaking) and one of the two official languages—along with Dutch—of the Brussels-Capital Region, where it is spoken by the majority of the population often as their primary language.
French is one of the four official languages of Switzerland (along with German, Italian, and Romansh) and is spoken in the western part of Switzerland, called Romandy, of which Geneva is the largest city. The language divisions in Switzerland do not coincide with political subdivisions, and some cantons have bilingual status: for example, cities such as Biel/Bienne and cantons such as Valais, Fribourg and Berne. French is the native language of about 23% of the Swiss population, and is spoken by 50.4% of the population.
French is also an official language of Monaco and Luxembourg, as well as in the Aosta Valley region of Italy, while French dialects remain spoken by minorities on the Channel Islands. It is also spoken in Andorra and is main communication language after Catalan in El Pas de la Casa. The language is taught as the primary second language in the German land of Saarland, with French being taught from pre-school and over 43% of citizens being able to speak French.
Africa
The majority of the world's French-speaking population lives in Africa. According to the 2007 report by the Organisation Internationale de la Francophonie, an estimated 115 million African people spread across 31 Francophone countries can speak French as either a first or a second language. This number does not include the people living in non-Francophone African countries who have learned French as a foreign language.Due to the rise of French in Africa, the total French-speaking population worldwide is expected to reach 700 million people in 2050. French is the fastest growing language on the continent (in terms of either official or foreign languages).
French is mostly a second language in Africa, but it has become a first language in some urban areas, such as the region of Abidjan, Ivory Coast and in Libreville, Gabon. There is not a single African French, but multiple forms that diverged through contact with various indigenous African languages.
Sub-Saharan Africa is the region where the French language is most likely to expand, because of the expansion of education and rapid population growth. It is also where the language has evolved the most in recent years. Some vernacular forms of French in Africa can be difficult to understand for French speakers from other countries, but written forms of the language are very closely related to those of the rest of the French-speaking world.
Americas
French is the second most common language in Canada, after English, and both are official languages at the federal level. It is the first language of 9.5 million people or 29% and the second language for 2.07 million or 6% of the entire population of Canada. French is the sole official language in the province of Quebec, being the mother tongue for some 7 million people, or almost 80% (2006 Census) of the province. About 95% of the people of Quebec speak French as either their first or second language, and for some as their third language. Quebec is also home to the city of Montreal, which is the world's 4th-largest French-speaking city, by number of first language speakers. New Brunswick and Manitoba are the only officially bilingual provinces, though full bilingualism is enacted only in New Brunswick, where about one third of the population is Francophone. French is also an official language of all of the territories (Northwest Territories, Nunavut, and Yukon). Out of the three, Yukon has the most French speakers, comprising just under 4% of the population.Furthermore, while French is not an official language in Ontario, the French Language Services Act ensures that provincial services are to be available in the language. The Act applies to areas of the province where there are significant Francophone communities, namely Eastern Ontario and Northern Ontario. Elsewhere, sizable French-speaking minorities are found in southern Manitoba, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island and the Port au Port Peninsula in Newfoundland and Labrador, where the unique Newfoundland French dialect was historically spoken. Smaller pockets of French speakers exist in all other provinces. The city of Ottawa, the Canadian capital, is also effectively bilingual, as it is on the other side of a river from Quebec, opposite the major city of Gatineau, and is required to offer governmental services in French as well as English.
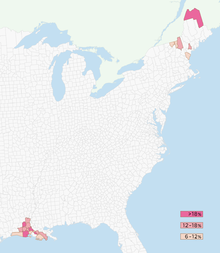
According to the U.S. Census Bureau (2011), French is the fourth most-spoken language in the United States after English, Spanish, and Chinese, when all forms of French are considered together and all dialects of Chinese are similarly combined. French remains the second most-spoken language in the states of Louisiana, Maine, Vermont and New Hampshire. Louisiana is home to many distinct dialects, collectively known as Louisiana French. According to the 2000 United States Census, there are over 194,000 people in Louisiana who speak French at home, the most of any state if Creole French is excluded. New England French, essentially a variant of Canadian French, is spoken in parts of New England. Missouri French was historically spoken in Missouri and Illinois (formerly known as Upper Louisiana), but is nearly extinct today.
French is one of Haiti's two official languages. It is the principal language of writing, school instruction, and administrative use. It is spoken by all educated Haitians and is used in the business sector. It is also used for ceremonial events such as weddings, graduations and church masses. About 70–80% of the country's population have Haitian Creole as their first language; the rest speak French as a first language. The second official language is the recently standardized Haitian Creole, which virtually the entire population of Haiti speaks. Haitian Creole is one of the French-based creole languages, drawing the large majority of its vocabulary from French, with influences from West African languages, as well as several European languages. Haitian Creole is closely related to Louisiana Creole and the creole from the Lesser Antilles.
French is the official language of both French Guiana on the South American continent, and of Saint Pierre and Miquelon, an archipelago off the coast of Newfoundland in North America.
Asia
Southeast Asia
French was the official language of the colony of French Indochina, comprising modern-day Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia. It continues to be an administrative language in Laos and Cambodia, although its influence has waned in recent years. In colonial Vietnam, the elites primarily spoke French, while many servants who worked in French households spoke a French pidgin known as "Tây Bồi" (now extinct). After French rule ended, South Vietnam continued to use French in administration, education, and trade. Since the Fall of Saigon and the opening of a unified Vietnam's economy, French has gradually been effectively displaced as the main foreign language of choice by English. French nevertheless maintains its colonial legacy by being spoken as a second language by the elderly and elite populations and is presently being revived in higher education and continues to be a diplomatic language in Vietnam. All three countries are official members of the OIF.
India
French is spoken in Pondicherry due to French rule in India.
Middle East
Lebanon
A former French colony, Lebanon designates Arabic as the sole official language, while a special law regulates cases when French can be publicly used. Article 11 of Lebanon's Constitution states that "Arabic is the official national language. A law determines the cases in which the French language is to be used".French language in Lebanon is widely used as a second language by the Lebanese people, and is taught in many schools as a secondary language along with Arabic and English. The language is also used on Lebanese pound bank notes, on road signs, on Lebanese license plates, and on official buildings (alongside Arabic).
Today, French and English are secondary languages of Lebanon, with about 40% of the population being Francophone and 40% Anglophone. The use of English is growing in the business and media environment. Out of about 900,000 students, about 500,000 are enrolled in Francophone schools, public or private, in which the teaching of mathematics and scientific subjects is provided in French. Actual usage of French varies depending on the region and social status. One third of high school students educated in French go on to pursue higher education in English-speaking institutions. English is the language of business and communication, with French being an element of social distinction, chosen for its emotional value. On social media, French was used on Facebook by just 10% of Lebanese in 2014, far behind English (78%).
Syria
Similarly to Lebanon, Syria was also a French League of Nations-mandate area until 1943, but today the French language is largely limited to some members of the elite and middle classes.
Israel
A significant French-speaking community is also present in Israel, primarily among the communities of French Jews in Israel, Moroccan Jews in Israel and Lebanese Jews. Many secondary schools offer French as a foreign language.
United Arab Emirates and Qatar
The UAE has the status in the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie as an observer state, and Qatar has the status in the organization as an associate state. However, in both countries French is not spoken by almost any of the general population or migrant workers, but spoken by a small minority of those who invest in Francophone countries or have other financial or family ties. Their entrance as observer and associate states respectively into the organisation was aided a good deal by their investments into the Organisation and France itself. A country's status as an observer state in the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie gives the country the right to send representatives to organization meetings and make formal requests to the organization but they do not have voting rights within the OIF. A country's status as an associate state also does not give a country voting abilities but associate states can discuss and review organization matters.
Oceania and Australasia
French is an official language of the Pacific Island nation of Vanuatu where 45% of the population can speak French. In the French special collectivity of New Caledonia, 97% of the population can speak, read and write French, whereas only 1% have no knowledge of French. In French Polynesia, 95% of the population can speak, read and write French, whereas only 1.5% have no knowledge of French. In the French collectivity of Wallis and Futuna, 78% of the population can speak, read and write French, whereas 17% have no knowledge of French.
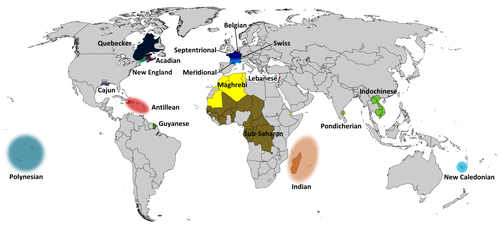
Dialects
- Acadian French
- African French including sub-branch Maghreb French (North African French)
- Aostan French
- Belgian French
- Cambodian French
- Canadian French
- Guianese French
- Haitian French
- Indian French
- Jersey Legal French
- Lao French
- Louisiana French
- Meridional French
- Metropolitan French
- Missouri French
- New Caledonian French
- Newfoundland French
- New England French
- Quebec French
- South East Asian French
- Swiss French
- Vietnamese French
- West Indian French
History
French is a Romance language (meaning that it is descended primarily from Vulgar Latin) that evolved out of the Gallo-Romance dialects spoken in northern France. The language's early forms include Old French and Middle French.
Vulgar Latin in Gallia
Due to Roman rule, Latin was gradually adopted by the inhabitants of Gaul, and as the language was learned by the common people it developed a distinct local character, with grammatical differences from Latin as spoken elsewhere, some of which being attested on graffiti. This local variety evolved into the Gallo-Romance tongues, which include French and its closest relatives, such as Arpitan.
The Celtic Gaulish language is thought to have survived into the 6th century in France, despite considerable Romanization. Coexisting with Latin, Gaulish helped shape the Vulgar Latindialects that developed into French, with effects including loanwords and calques (including oui, the word for "yes"), sound changes shaped by Gaulish influence, and influences in conjugation and word order. Recent computational studies suggest that early gender shifts may have been motivated by the gender of the corresponding word in Gaulish.
Old French
The beginning of French in Gaul was greatly influenced by Germanic invasions into the country. These invasions had the greatest impact on the northern part of the country and on the language there. A language divide began to grow across the country. The population in the north spoke langue d'oïl while the population in the south spoke langue d'oc. Langue d'oïl grew into what is known as Old French. The period of Old French spanned between the 8th and 14th centuries. Old French shared many characteristics with Latin. For example, Old French made use of all possible word orders just as Latin did.
Middle French
Within Old French many dialects emerged but the Francien dialect is one that not only continued but also thrived during the Middle French period (14th century–17th century). Modern French grew out of this Francien dialect. Grammatically, during the period of Middle French, noun declensions were lost and there began to be standardized rules. Robert Estiennepublished the first Latin-French dictionary, which included information about phonetics, etymology, and grammar. Politically, the Ordinance of Villers-Cotterêts (1539) named French the language of law.
Modern French
During the 17th century, French replaced Latin as the most important language of diplomacy and international relations (lingua franca). It retained this role until approximately the middle of the 20th century, when it was replaced by English as the United States became the dominant global power following the Second World War. Stanley Meisler of the Los Angeles Timessaid that the fact that the Treaty of Versailles was written in English as well as French was the "first diplomatic blow" against the language.
During the Grand Siècle (17th century), France, under the rule of powerful leaders such as Cardinal Richelieu and Louis XIV, enjoyed a period of prosperity and prominence among European nations. Richelieu established the Académie française to protect the French language. By the early 1800s, Parisian French had become the primary language of the aristocracy in France.
Near the beginning of the 19th century, the French government began to pursue policies with the end goal of eradicating the many minority and regional languages (Patois) spoken in France. This began in 1794 with Henri Grégoire's "Report on the necessity and means to annihilate the patois and to universalise the use of the French language". When public education was made compulsory, only French was taught and the use of any other (Patois) language was punished. The goals of the Public School System were made especially clear to the French speaking teachers sent to teach students in regions such as Occitania and Brittany: "And remember, Gents: you were given your position in order to kill the Breton language" were instructions given from a French official to teachers in the French department of Finistère (western Brittany). The prefect of Basses-Pyrénées in the French Basque Country wrote in 1846: "Our schools in the Basque Country are particularly meant to substitute the Basque language with French...". Students were taught that their ancestral languages were inferior and they should be ashamed of them; this process was known in the Occitan-speaking region as Vergonha.
Among the historic reformers of French language, such as Louis Maigret, Marle M., Marcelin Berthelot, Philibert Monet, Jacques Peletier du Mans, Somaize, nowadays the most striking reform is proposed by Mickael Korvin, a Franco-American linguist of Hungarian origin who wants to eliminate accents, silent letters, double letters and more.
Current status and economic, cultural and institutional importance
Spoken on all continents (like English, Spanish, and Portuguese), French is taught in universities around the world, and is one of the world's most influential languages because of its wide use in the worlds of journalism, jurisprudence, the academy, and diplomacy. In diplomacy, French is one of the six official languages of the United Nations (and one of the UN Secretariat's only two working languages), one of twenty official and three working languages of the European Union, an official language of NATO, the International Olympic Committee, the Council of Europe, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Organization of American States (alongside Spanish, Portuguese and English), the Eurovision Song Contest, one of eighteen official languages of the European Space Agency, World Trade Organisation and the least used of the three official languages in the North American Free Trade Agreement countries. It is also a working language in nonprofit organisations such as the Red Cross (alongside English, German, Spanish, Portuguese, Arabic and Russian), Amnesty International (alongside 32 other languages of which English is the most used, followed by Spanish, Portuguese, German, and Italian, Médecins sans Frontières (used alongside English, Spanish, Portuguese and Arabic), and Médecins du Monde (used alongside English). Given the demographic prospects of the French-speaking nations of Africa, Forbes released an article in 2014 which claimed that French "could be the language of the future".
Significant as a judicial language, French is one of the official languages of such major international and regional courts, tribunals, and dispute-settlement bodies as the African Court on Human and Peoples' Rights, the Caribbean Court of Justice, the Court of Justice for the Economic Community of West African States, the Inter-American Court of Human Rights, the International Court of Justice, the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia, International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda, the International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea the International Criminal Court and the World Trade Organization Appellate Body. It is the sole internal working language of the Court of Justice of the European Union, and makes with English the European Court of Human Rights's two working languages.
In 1997, George Werber published, in Language Today, a comprehensive academic study entitled "The World's 10 most influential languages". In the article, Werber ranked French as, after English, the second most influential language of the world, ahead of Spanish. His criteria were the numbers of native speakers, the number of secondary speakers (especially high for French among fellow world languages), the number of countries using the language and their respective populations, the economic power of the countries using the language, the number of major areas in which the language is used, and the linguistic prestige associated with the mastery of the language (Werber highlighted that French in particular enjoys considerable linguistic prestige). In a 2008 reassessment of his article, Werber concluded that his findings were still correct since "the situation among the top ten remains unchanged."
Knowledge of French is often considered to be a useful skill by business owners in the United Kingdom; a 2014 study found that 50% of British managers considered French to be a valuable asset for their business, thus ranking French as the most-sought after foreign language there, ahead of German (49%) and Spanish (44%). MIT economist Albert Saiz calculated a 2.3% premium for those who have French as a foreign language in the workplace.
In English-speaking Canada, the United Kingdom, and the Republic of Ireland, French retains the privilege of being the first foreign language taught and in number of pupils is far ahead of other languages. In the United States, Spanish is the most commonly taught foreign language, though French is next.
The future of the French language is often discussed in the news—for example, in a recent media debate in New York City. In 2014, The New York Times documented an increase in the teaching of French in New York, especially in bilingual programs where only Spanish and Mandarin are now offered more than French. A few days later, the linguist John McWhorterlaunched a frontal attack on the article on his blog at The New Republic. He stressed that learning French in the United States is anchored in an outdated view of French as the most widely spoken language in Europe at a time when U.S. immigration from outside Europe was limited. McWhorter argued that young Americans should learn languages such as Mandarin, Spanish, Arabic or Hindi. However, in a study published in March 2014 by Forbes magazine, the investment bank Natixis said that French could become the world's most spoken language by 2050. It noted that French is spreading in areas where the population is rapidly increasing, especially in sub-Saharan Africa.
Phonology
There are a maximum of 17 vowels in French, not all of which are used in every dialect: /a/, /ɑ/, /e/, /ɛ/, /ɛː/, /ə/, /i/, /o/, /ɔ/, /y/, /u/, /œ/, /ø/, plus the nasalized vowels /ɑ̃/, /ɛ̃/, /ɔ̃/ and /œ̃/. In France, the vowels /ɑ/, /ɛː/ and /œ̃/ are tending to be replaced by /a/, /ɛ/ and /ɛ̃/ in many people's speech, but the distinction of /ɛ̃/ and /œ̃/ is present in Meridional French. In Quebec and Belgian French, the vowels /ɑ/, /ə/, /ɛː/ and /œ̃/ are present.Although there are many French regional accents, foreign learners normally use only one variety of the language.
- Voiced stops (i.e., /b, d, ɡ/) are typically produced fully voiced throughout.
- Voiceless stops (i.e., /p, t, k/) are unaspirated.
- Nasals: The velar nasal /ŋ/ can occur in final position in borrowed (usually English) words: parking, camping, swing. The palatal nasal /ɲ/ can occur in word initial position (e.g., gnon), but it is most frequently found in intervocalic, onset position or word-finally (e.g., montagne).
- Fricatives: French has three pairs of homorganic fricatives distinguished by voicing, i.e., labiodental /f/~/v/, dental /s/~/z/, and palato-alveolar /ʃ/~/ʒ/. Notice that /s/~/z/ are dental, like the plosives /t/~/d/ and the nasal /n/.
- French has one rhotic whose pronunciation varies considerably among speakers and phonetic contexts. In general, it is described as a voiced uvular fricative, as in [ʁu] roue, "wheel". Vowels are often lengthened before this segment. It can be reduced to an approximant, particularly in final position (e.g., fort), or reduced to zero in some word-final positions. For other speakers, a uvular trill is also common, and an apical trill [r] occurs in some dialects.
- Lateral and central approximants: The lateral approximant /l/ is unvelarised in both onset (lire) and coda position (il). In the onset, the central approximants [w], [ɥ], and [j] each correspond to a high vowel, /u/, /y/, and /i/ respectively. There are a few minimal pairs where the approximant and corresponding vowel contrast, but there are also many cases where they are in free variation. Contrasts between /j/ and /i/ occur in final position as in /pɛj/ paye, "pay", vs. /pɛi/ pays, "country".
French pronunciation follows strict rules based on spelling, but French spelling is often based more on history than phonology. The rules for pronunciation vary between dialects, but the standard rules are:
- final consonants: Final single consonants, in particular s, x, z, t, d, n, p and g, are normally silent. (A consonant is considered "final" when no vowel follows it even if one or more consonants follow it.) The final letters f, k, q, and l, however, are normally pronounced. The final c is sometimes pronounced like in bac, sac, roc but can also be silent like in blanc or estomac. The final r is usually silent when it follows an e in a word of two or more syllables, but it is pronounced in some words (hiver, super, cancer etc.).
- When the following word begins with a vowel, however, a silent consonant may once again be pronounced, to provide a liaison or "link" between the two words. Some liaisons are mandatory, for example the s in les amants or vous avez; some are optional, depending on dialect and register, for example, the first s in deux cents euros or euros irlandais; and some are forbidden, for example, the s in beaucoup d'hommes aiment. The t of et is never pronounced and the silent final consonant of a noun is only pronounced in the plural and in set phrases like pied-à-terre.
- Doubling a final n and adding a silent e at the end of a word (e.g., chien → chienne) makes it clearly pronounced. Doubling a final l and adding a silent e (e.g., gentil → gentille) adds a [j] sound if the l is preceded by the letter i.
- elision or vowel dropping: Some monosyllabic function words ending in a or e, such as je and que, drop their final vowel when placed before a word that begins with a vowel sound (thus avoiding a hiatus). The missing vowel is replaced by an apostrophe. (e.g., *je ai is instead pronounced and spelled → j'ai). This gives, for example, the same pronunciation for l'homme qu'il a vu ("the man whom he saw") and l'homme qui l'a vu ("the man who saw him"). However, for Belgian French the sentences are pronounced differently; in the first sentence the syllable break is as "qu'il-a", while the second breaks as "qui-l'a". It can also be noted that, in Quebec French, the second example (l'homme qui l'a vu) is more emphasized on l'a vu.
Writing system
Alphabet
French is written with the 26 letters of the basic Latin script, with four diacritics appearing on vowels (circumflex accent, acute accent, grave accent, diaeresis) and the cedilla appearing in "ç".
There are two ligatures, "œ" and "æ", but they are now often not used because of the layout of the most common keyboards used in French-speaking countries. Yet, they cannot be changed for "oe" and "ae" in formal and literary texts.
Orthography
French spelling, like English spelling, tends to preserve obsolete pronunciation rules. This is mainly due to extreme phonetic changes since the Old French period, without a corresponding change in spelling. Moreover, some conscious changes were made to restore Latin orthography (as with some English words such as "debt"):
- Old French doit > French doigt "finger" (Latin digitus)
- Old French pie > French pied "foot" [Latin pes (stem: ped-)]
French is a morphophonemic language. While it contains 130 graphemes that denote only 36 phonemes, many of its spelling rules are likely due to a consistency in morphemic patterns such as adding suffixes and prefixes. Many given spellings of common morphemes usually lead to a predictable sound. In particular, a given vowel combination or diacritic generally leads to one phoneme. However, there is not a one to one correlation from a phoneme to its related grapheme, which can be seen in how tomber, tombai, and tombé all end with the /E/ phoneme.Additionally, there are many variations in the pronunciation of consonants at the end of words, demonstrated by how the x in paix is not pronounced though at the end of Aix it is.
As a result, it can be difficult to predict the spelling of a word based on the sound. Final consonants are generally silent, except when the following word begins with a vowel (see Liaison (French)). For example, the following words end in a vowel sound: pied, aller, les, finit, beaux. The same words followed by a vowel, however, may sound the consonants, as they do in these examples: beaux-arts, les amis, pied-à-terre.
French writing, as with any language, is affected by the spoken language. In Old French, the plural for animal was animals. The /als/ sequence was unstable and was turned into a diphthong /aus/. This change was then reflected in the orthography: animaus. The us ending, very common in Latin, was then abbreviated by copyists (monks) by the letter x, resulting in a written form animax. As the French language further evolved, the pronunciation of au turned into /o/ so that the u was reestablished in orthography for consistency, resulting in modern French animaux(pronounced first /animos/ before the final /s/ was dropped in contemporary French). The same is true for cheval pluralized as chevaux and many others. In addition, castel pl. castels became château pl. châteaux.
- Nasal: n and m. When n or m follows a vowel or diphthong, the n or m becomes silent and causes the preceding vowel to become nasalized (i.e., pronounced with the soft palate extended downward so as to allow part of the air to leave through the nostrils). Exceptions are when the n or m is doubled, or immediately followed by a vowel. The prefixes en- and em- are always nasalized. The rules are more complex than this but may vary between dialects.
- Digraphs: French uses not only diacritics to specify its large range of vowel sounds and diphthongs, but also specific combinations of vowels, sometimes with following consonants, to show which sound is intended.
- Gemination: Within words, double consonants are generally not pronounced as geminates in modern French (but geminates can be heard in the cinema or TV news from as recently as the 1970s, and in very refined elocution they may still occur). For example, illusion is pronounced [ilyzjɔ̃] and not [ilːyzjɔ̃]. But gemination does occur between words. For example, une info ("a news item" or "a piece of information") is pronounced [ynɛ̃fo], whereas une nympho ("a nymphomaniac") is pronounced [ynːɛ̃fo].
- Accents are used sometimes for pronunciation, sometimes to distinguish similar words, and sometimes based on etymology alone.
- Accents that affect pronunciation
- The acute accent (l'accent aigu) é (e.g., école—school) means that the vowel is pronounced /e/ instead of the default /ə/.
- The grave accent (l'accent grave) è (e.g., élève—pupil) means that the vowel is pronounced /ɛ/ instead of the default /ə/.
- The circumflex (l'accent circonflexe) ê (e.g. forêt—forest) shows that an e is pronounced /ɛ/ and that an ô is pronounced /o/. In standard French, it also signifies a pronunciation of /ɑ/ for the letter â, but this differentiation is disappearing. In the mid-18th century, the circumflex was used in place of s after a vowel, where that letter swas not pronounced. Thus, forest became forêt, hospital became hôpital, and hostel became hôtel.
- The diaeresis (le tréma) (e.g., naïf—naive, Noël—Christmas) as in English, specifies that this vowel is pronounced separately from the preceding one, not combined, and is not a schwa.
- The cedilla (la cédille) ç (e.g., garçon—boy) means that the letter ç is pronounced /s/ in front of the back vowels a, o and u (c is otherwise /k/ before a back vowel). C is always pronounced /s/ in front of the front vowels e, i, and y, thus ç is never found in front of front vowels.
- Accents with no pronunciation effect
- The circumflex does not affect the pronunciation of the letters i or u, nor, in most dialects, a. It usually indicates that an s came after it long ago, as in île (isle, compare with English island). The explanation is that some words share the same orthography, so the circumflex is put here to mark the difference between the two words. For example, dites (you say) / dîtes (you said), or even du (of the) / dû (past for the verb devoir = must, have to, owe; in this case, the circumflex disappears in the plural and the feminine).
- All other accents are used only to distinguish similar words, as in the case of distinguishing the adverbs là and où ("there", "where") from the article la ("the" feminine singular) and the conjunction ou ("or"), respectively.
- Accents that affect pronunciation
Some proposals exist to simplify the existing writing system, but they still fail to gather interest.
In 1990, a reform accepted some changes to French orthography. At the time the proposed changes were considered to be suggestions. In 2016, schoolbooks in France began to use the newer recommended spellings, with instruction to teachers that both old and new spellings be deemed correct.
Grammar
French is a moderately inflected language. Nouns and most pronouns are inflected for number (singular or plural, though in most nouns the plural is pronounced the same as the singular even if spelled differently); adjectives, for number and gender (masculine or feminine) of their nouns; personal pronouns and a few other pronouns, for person, number, gender, and case; and verbs, for tense, aspect, mood, and the person and number of their subjects. Case is primarily marked using word order and prepositions, while certain verb features are marked using auxiliary verbs. According to the French lexicogrammatical system, French has a rank-scale hierarchy with clause as the top rank, which is followed by group rank, word rank, and morpheme rank. A French clause is made up of groups, groups are made up of words, and lastly, words are made up of morphemes.
French grammar shares several notable features with most other Romance languages, including
- the loss of Latin declensions
- only two grammatical genders
- the development of grammatical articles from Latin demonstratives
- new tenses formed from auxiliaries
Nouns
Every French noun is either masculine or feminine. Because French nouns are not inflected for gender, a noun's form cannot specify its gender. For nouns regarding the living, their grammatical genders often correspond to that which they refer to. For example, a male teacher is a "enseignant" while a female teacher is a "enseignante." However, plural nouns that refer to a group that includes both masculine and feminine entities are always masculine. So a group of two male teachers would be "enseignants." A group of two male teachers and two female teachers would still be "enseignants." In many situations, and in the case of "enseignant," both the singular and plural form of a noun are pronounced identically. The article used for singular nouns is different from that used for plural nouns and the article provides a distinguishing factor between the two in speech. For example, the singular "le professeur" or "la professeur(e)" (the male or female teacher, professor) can be distinguished from the plural "les professeurs" because "le," "la," and "les" are all pronounced differently. There are some situations where both the feminine and masculine form of a noun are the same and the article provides the only difference. For example, "le dentiste" refers to a male dentist while "la dentiste" refers to a female dentist.
Verbs
Moods and tense-aspect forms
The French language consists of both finite and non-finite moods. The finite moods include the indicative mood (indicatif), the subjunctive mood (subjonctif), the imperative mood, (imperatif), and the conditional mood (conditionnel). The non-finite moods include the infinitive mood (infinitif), the present participle (participe présent), and the past participle (participe passé).
Finite moods
Indicative (Indicatif)
The indicative mood makes use of eight different tense-aspect forms. These include the present (présent), the simple past (passé composé and passé simple), the past imperfective (imparfait), the pluperfect (plus-que-parfait), the simple future (futur simple), the future perfect (futur antérieur), and the past perfect (passé antérieur). Some forms are less commonly used today. In today's spoken French, the passé composé is used while the passé simple is reserved for formal situations or for literary purposes. Similarly, the plus-que-parfait is used for speaking rather than the older passé antérieur seen in literary works.
Within the indicative mood, the passé composé, plus-que-parfait, futur antérieur, and passé antérieur all use auxiliary verbs in their forms.
| Indicatif | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Présent | Imparfait | Passé composé | Passé simple | |||||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| 1st Person | j'aime | nous aimons | j'aimais | nous aimions | j'ai aimé | nous avons aimé | j'aimai | nous aimâmes |
| 2nd Person | tu aimes | vous aimez | tu aimais | vous aimiez | tu as aimé | vous avez aimé | tu aimas | vous aimâtes |
| 3rd Person | il/elle aime | ils/elles aiment | il/elle aimait | ils/elles aimaient | il/elle a aimé | ils/elles ont aimé | il/elle aima | ils/elles aimèrent |
| Futur simple | Futur antérieur | Plus-que-parfait | Passé antérieur | |||||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| 1st Person | j'aimerai | nous aimerons | j'aurai aimé | nous aurons aimé | j'avais aimé | nous avions aimé | j'eus aimé | nous eûmes aimé |
| 2nd Person | tu aimeras | vous aimerez | tu auras aimé | vous aurez aimé | tu avais aimé | vous aviez aimé | tu eus aimé | vous eûtes aimé |
| 3rd Person | il/elle aimera | ils/elles aimeront | il/elle aura aimé | ils/elles auront aimé | il/elle avais aimé | ils/elles avaient aimé | il/elle eut aimé | ils/elles eurent aimé |
Subjunctive (Subjonctif)
The subjunctive mood only includes four of the tense-aspect forms found in the indicative: present (présent), simple past (passé composé), past imperfective (imparfait), and pluperfect (plus-que-parfait).
Within the subjunctive mood, the passé composé and plus-que-parfait use auxiliary verbs in their forms.
| Subjonctif | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Présent | Imparfait | Passé composé | Plus-que-parfait | |||||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| 1st Person | j'aime | nous aimions | j'aimasse | nous aimassions | j'aie aimé | nous ayons aimé | j'eusse aimé | nous eussions aimé |
| 2nd Person | tu aimes | vous aimiez | tu aimasses | vous aimassiez | tu aies aimé | vous ayez aimé | tu eusses aimé | vous eussiez aimé |
| 3rd Person | il/elle aime | ils/elles aiment | il/elle aimât | ils/elles aimassent | il/elle ait aimé | ils/elles aient aimé | il/elle eût aimé | ils/elles eussent aimé |
The imperative is used in the present tense (with the exception of a few instances where it is used in the perfect tense). The imperative is used to give commands to you (tu), we/us (nous), and plural you (vous).
| Imperatif | ||
|---|---|---|
| Présent | ||
| Singular | Plural | |
| 1st Person | aimons | |
| 2nd Person | aime | aimez |
Conditional (Conditionnel)
The conditional makes use of the present (présent) and the past (passé).
The passé uses auxiliary verbs in its forms.
| Conditionnel | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Présent | Passé | |||
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| 1st Person | j'aimerais | nous aimerions | j'aurais aimé | nous aurions aimé |
| 2nd Person | tu aimerais | vous aimeriez | tu aurais aimé | vous auriez aimé |
| 3rd Person | il/elle aimerait | ils/elles aimeraient | il/elle aurait aimé | ils/elles auraient aimé |
Non-Finite moods
Infinitive (Infinitif)
The infinitive can be used in both the present and the past.
| Infinitif | |
|---|---|
| Présent | Passé |
| aimer | avoir aimé |
Present participle (Participe présent)
The present participle uses the present tense but can also be found in the past.
| Participe Présent | |
|---|---|
| Présent | Passé |
| aimant | ayant aimé |
Past participle (Participe passé)
The past participle is found in the past.
| Participe Passé |
|---|
| aimé |
Voice
French uses both the active voice and the passive voice. The active voice is unmarked while the passive voice is formed by using a form of verb être ("to be") and the past participle.
Example of the active voice:
- "Elle aime le chien." She loves the dog.
- "Mark a conduit la voiture." Mark drove the car.
Example of the passive voice:
- "Le chien est aimé par elle." The dog is loved by her.
- "La voiture était conduite par Mark." The car was driven by Mark.
Syntax
Word order
French declarative word order is subject–verb–object although a pronoun object precedes the verb. Some types of sentences allow for or require different word orders, in particular inversionof the subject and verb like "Parlez-vous français?" when asking a question rather than just "Vous parlez français ?" Both questions mean the same thing; however, a rising inflection is always used on both of them whenever asking a question, especially on the second one. Specifically, the first translates into "Do you speak French?" while the second one is literally just "You speak French?" To avoid inversion while asking a question, 'Est-ce que' (literally 'is it that') may be placed in the beginning of the sentence. "Parlez-vous français ?" may become "Est-ce que vous parlez français ?" French also uses verb–object–subject (VOS) and object–subject–verb (OSV) word order. OSV word order is not used often and VOS is reserved for formal writings.
Vocabulary
The majority of French words derive from Vulgar Latin or were constructed from Latin or Greek roots. In many cases a single etymological root appears in French in a "popular" or native form, inherited from Vulgar Latin, and a learned form, borrowed later from Classical Latin. The following pairs consist of a native noun and a learned adjective:
- brother: frère / fraternel from Latin frater / fraternalis
- finger: doigt / digital from Latin digitus / digitalis
- faith: foi / fidèle from Latin fides / fidelis
- eye: œil / oculaire from Latin oculus / ocularis
However, a historical tendency to gallicise Latin roots can be identified, whereas English conversely leans towards a more direct incorporation of the Latin:
- rayonnement / radiation from Latin radiatio
- éteindre / extinguish from Latin exstinguere
- noyau / nucleus from Latin nucleus
- ensoleillement / insolation from Latin insolatio
There are also noun-noun and adjective-adjective pairs:
- thing/cause: chose / cause from Latin causa
- cold: froid / frigide from Latin frigidum
It can be difficult to identify the Latin source of native French words, because in the evolution from Vulgar Latin, unstressed syllables were severely reduced and the remaining vowels and consonants underwent significant modifications.
More recently the linguistic policy of the French language academies of France and Quebec has been to provide French equivalents to (mainly English) imported words, either by using existing vocabulary, extending its meaning or deriving a new word according to French morphological rules. The result is often two (or more) co-existing terms for describing the same phenomenon.
Root Languages for Words of Foreign Origin
English (25.095%)
Italian (16.833%)
Germanic Languages(13.095%)
Gallo-Romance Languages (11.452%)
Arabic (5.119%)
German (3.905%)
Celtic Languages (3.810%)
Spanish (3.810%)
Dutch (3.643%)
Persian and Sanskrit (2.667%)
Native American Languages(2.405%)
Asian Languages (2.119%)
Afro-Asian Languages (1.333%)
Slavic and Baltic Languages(1.310%)
Basque (0.238%)
Other Languages (3.429%)
- mercatique / marketing
- finance fantôme / shadow banking
- bloc-notes / notepad
- ailière / wingsuit
- tiers-lieu / coworking
It is estimated that 12% (4,200) of common French words found in a typical dictionary such as the Petit Larousse or Micro-Robert Plus (35,000 words) are of foreign origin (where Greek and Latin learned words are not seen as foreign). About 25% (1,054) of these foreign words come from English and are fairly recent borrowings. The others are some 707 words from Italian, 550 from ancient Germanic languages, 481 from other Gallo-Romance languages, 215 from Arabic, 164 from German, 160 from Celtic languages, 159 from Spanish, 153 from Dutch, 112 from Persian and Sanskrit, 101 from Native American languages, 89 from other Asian languages, 56 from other Afro-Asiatic languages, 55 from Slavic languages and Baltic languages, 10 from Basque and 144 (about 3%) from other languages.
One study analyzing the degree of differentiation of Romance languages in comparison to Latin estimated that among the languages analyzed French has the greatest distance from Latin. Lexical similarity is 89% with Italian, 80% with Sardinian, 78% with Rhaeto-Romance, and 75% with Romanian, Spanish and Portuguese.
Numerals
The French counting system is partially vigesimal: twenty (vingt) is used as a base number in the names of numbers from 80 to 99. The French word for 80 is quatre-vingts, literally "four twenties", and the word for 75 is soixante-quinze, literally "sixty-fifteen". This reform arose after the French Revolutionto unify the different counting systems (mostly vigesimal near the coast, because of Celtic (via Breton) and Viking influences). This system is comparable to the archaic English use of score, as in "fourscore and seven" (87), or "threescore and ten" (70).
In Old French (during the Middle Ages), all numbers from 30 to 99 could be said in either base 10 or base 20, e.g. vint et doze (twenty and twelve) for 32, dous vinz et diz (two twenties and ten) for 50, uitante for 80, or nonante for 90.
Belgian French, Swiss French, Aostan French and the French used in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda and Burundi are different in this respect. In the French spoken in these places, 70 and 90 are septante and nonante. In Switzerland, depending on the local dialect, 80 can be quatre-vingts(Geneva, Neuchâtel, Jura) or huitante (Vaud, Valais, Fribourg). Octante had been used in Switzerland in the past, but is now considered archaic, while in the Aosta Valley 80 is huitante. In Belgium and in its former African colonies, however, quatre-vingts is universally used.
French, like most European languages, uses a space to separate thousands where English uses a comma or (more recently) a space. The comma is used in French numbers as a decimal point: 2,5 = deux virgule cinq.
Units
Cardinal numbers in French, from 0 to 20, are as follows:
- Zero: zéro /ze.ʁo/
- One: un/une /œ̃/ (m) ~ /yn/ (f)
- Two: deux /dø/
- Three: trois /tʁwɑ/
- Four: quatre /katʁ/
- Five: cinq /sɛ̃k/
- Six: six /sis/
- Seven: sept /sɛt/
- Eight: huit /ɥit/
- Nine: neuf /nœf/
- Ten: dix /dis/
- Eleven: onze /ɔ̃z/
- Twelve: douze /duz/
- Thirteen: treize /tʁɛz/
- Fourteen: quatorze /katɔʁz/
- Fifteen: quinze /kɛ̃z/
- Sixteen: seize /sɛz/
- Seventeen: dix-sept /dissɛt/
- Eighteen: dix-huit /diz‿ɥit/
- Nineteen: dix-neuf /diznœf/
- Twenty: vingt /vɛ̃/
After Twenty, numbers use base ten logic (vingt et un, vingt-deux, vingt-trois...)
Tens
Cardinal numbers in French, by tens from 10 to 100, are as follows:
- Ten: dix /dis/
- Twenty: vingt /vɛ̃/
- Thirty: trente /tʁɑ̃t/
- Forty: quarante /ka.ʁɑ̃t/
- Fifty: cinquante /sɛ̃.kɑ̃t/
- Sixty: soixante /swa.sɑ̃t/
- Seventy: soixante-dix /swa.sɑ̃t.dis/ or septante /sɛp.tɑ̃t/
- Eighty: quatre-vingts /ka.tʁɘ.vɛ̃/, huitante /ɥi.tɑ̃t/ or octante /ɔk.tɑ̃t/
- Ninety: quatre-vingt-dix /ka.tʁɘ.vɛ̃.dis/ or nonante /nɔ.nɑ̃t/
- One hundred: cent /sɑ̃(t)/
After One hundred, numbers use base ten logic (cent dix, cent vingt, cent trente...)
Hundreds
Cardinal numbers in French, by hundreds from 100 to 2000, are as follows:
- One hundred: cent /sɑ̃(t)/
- Two hundred: deux cents
- Three hundred: trois cents, (Archaism: quinze-vingts)
- Four hundred: quatre cents
- Five hundred: cinq cents
- Six hundred: six cents
- Seven hundred: sept cents
- Eight hundred: huit cents
- Nine hundred: neuf cents
- One thousand: mille
- One thousand one hundred: onze cents or mille cent
- One thousand two hundred: douze cents or mille deux cents
- One thousand three hundred: treize cents or mille trois cents
- One thousand four hundred: quatorze cents or mille quatre cents
- One thousand five hundred: quinze cents or mille cinq cents
- One thousand six hundred: seize cents or mille six cents
- One thousand seven hundred: dix-sept cents or mille sept cents
- One thousand eight hundred: dix-huit cents or mille huit cents
- One thousand nine hundred: dix-neuf cents or mille neuf cents
- Two thousand: deux mille
After deux mille (2000), only the second option is used (deux mille cent, deux mille deux cents, deux mille trois cents...)
The words vingt and cent take the plural -s only when they are the last word of the number: quatre-vingts (eighty) and quatre-vingt-un (eighty-one), cinq cents (five hundred) and cinq cent trente (five hundred and thirty). When a number using vingt or cent is used as an ordinal numeral adjective, the words vingt or cent stay unchanged.
Scales
Cardinal numbers in French, by exponentiation points, from 10 to 10, are as follows:
- One: un/une /œ̃/ (m) ~ /yn/ (f)
- Ten: dix /dis/
- One hundred: cent /sɑ̃(t)/
- One thousand: mille /mil/
- Ten thousand: dix mille
- Hundred thousand: cent mille
- One million: un million /mi.ljɔ̃/
- Ten million: dix millions
- Hundred million: cent millions
- One billion: un milliard
- Ten billion: dix milliards
- Hundred billion: cent milliards
- One trillion: un billion /bi.ljɔ̃/
- Ten trillion: dix billions
- Hundred trillion: cent billions
- One quadrillion: un billiard
- Ten quadrillion: dix billiards
- Hundred quadrillion: cent billiards
- One quintillion: un trillion
- Ten quintillion: dix trillions
- Hundred quintillion: cent trillions
- It has been suggested that Nine and New homophonographs are related and that it would be an unusual preservation of the octal number system speculated to be formerly used in proto-Indo-European language, though the evidence supporting this is slim.
- Septante is used in Belgium and in Switzerland. Its use is dated in Eastern France and archaic elsewhere in France.
- Huitante is used in Vaud, Valais, Fribourg, archaic in France.
- Octante is used, but dated, in Romandie and in Southern France. Its use is archaic in other parts of France.
- Nonante is used in Belgium, Switzerland and, dated, in Eastern France, archaic in other parts of France.
- Formerly singular of the now invariable mille, mil is now only used in formal documents to write dates between mil un (1001) and mil neuf cent quatre-vingt-dix-neuf (1999).
- While both styles are correct and concurrently used, numbers above mille and under deux mille are usually counted by hundreds from onze cents up to seize cent quatre-vingt-dix-neufand are then indifferently counted both styles in informal language while the count by adding hundreds to one thousand, like in mille cent, mille six cents, is favoured in written language, especially in juridical, administrative and scientific works.
- Nota Bene that English use the short scale while French use the long scale.
Words
| English | French | Quebec accent | Touraine accent |
|---|---|---|---|
| French | Français (people) or français (language) | [fʁ̥ãsɛ] | [fʁ̥ɒ̃sɛ] |
| English | Anglais (people) or anglais (language) | [ãɡlɛ] | [ɒ̃ɡlɛ] |
| Yes | Oui (si when countering an assertion or a question expressed in the negative) | [wi] | [wi] |
| No | Non | [nɔ̃] | [nõ] |
| Hello! | Bonjour ! (formal) or Salut ! (informal) or "Allô" (Quebec French or when answering on the telephone) | [bõʒuːʁ] | [bõʒuʁ] |
| Good evening! | Bonsoir ! | [bõswɑːʁ] | [bõswaʁ] |
| Good night! | Bonne nuit ! | [bɔn nɥi] | [bʌn nɥi] |
| Goodbye! | Au revoir ! | [ɔʁvwɑːʁ] | [oʁ(ø)vwaʁ] |
| Have a nice day! | Bonne journée ! | [bɔn ʒuʁne] | [bʌn ʒuʁne] |
| Please/if you please | S’il vous plaît (formal) or S’il te plaît (informal) | [sɪl vu plɛ] | [sil vu plɛ] |
| Thank you | Merci | [mɛʁsi] | [mɛʁ̥si] |
| You are welcome | De rien (informal) or Ce n’est rien (informal) ("it is nothing") or Je vous en prie (formal) or Je t’en prie(informal) or Bienvenue (Quebec) | [də ʁjẽ] | [dœ ʁjæ̃] |
| I am sorry | Pardon or Désolé or Je suis désolé (if male) / Je suis désolée (if female) or Excuse-moi (informal) / Excusez-moi (formal) / "Je regrette" | [paʁdɒ̃] / [dezɔle] | [paʁdõ] / [dezɔle] |
| Who? | Qui ? | [ki] | [ki] |
| What? | Quoi ? (←informal; used as "What?" in English) or Pardon ? (←formal; used the same as "Excuse me?" in English) | [kwa] | [kwa] |
| When? | Quand ? | [kæ̃] | [kɒ̃] |
| Where? | Où ? | [u] | [u] |
| Why? | Pourquoi ? | [puʁ̥kwa] | [puʁ̥kwa] |
| What is your name? | Comment vous appelez-vous ? (formal) or Comment t’appelles-tu ? (informal) | [kɔmã vu z‿aple vu], [kɔmã t‿apɛl t͡sy] | [kɔmɒ̃ vu z‿aple vu], [kɔmɒ̃ t‿apɛl ty] |
| My name is... | Je m'appelle... | [ʒø mapɛl] | |
| Which | Quel/Quels(pl.)/Quelle(fem.) | [kɛl] | [kɛl] |
| Because | Parce que / Car | [paʁ̥skœ] | [paʁ̥s(ø)kø] |
| Because of | À cause de | [a kou̯z dœ] | [a koz dø] |
| Therefore, so | Donc | [dõːk] | [dõk] |
| Maybe | Peut-être | [pœt‿aɪ̯tʀ̥] | [pøt‿ɛtʁ̥] |
| How? | Comment ? | [kɔmã] | [kɔmɒ̃] |
| How much? | Combien ? | [kõbjẽ] | [kõbjæ̃] |
| I do not understand. | Je ne comprends pas. | [ʒœ nœ kõpʁ̥ã pɔ] | [ʒø nø kõpʁ̥ɒ̃ pa] |
| Yes, I understand. | Oui, je comprends. Except when responding to a negatively posed question, in which case Si is used preferentially over Oui | [wi ʒœ kõpʁ̥ã] | [wi ʒø kõpʁ̥ɒ̃] |
| I agree | Je suis d’accord. "D’accord" can be used without je suis. | [ʒə sɥi dakɑɔ̯ʁ] | [ʒø sɥi dakɔʁ] |
| Help! | Au secours ! (à l’aide !) | [o skuːʁ] | [o søkuːʁ] |
| At what time...? | À quelle heure...? | [a kɛl aœ̯ʁ] | [a kɛl œʁ] |
| Today | Aujourd'hui | [oʒuʁd͡zɥi] | [oʒuʁdɥi] |
| Can you help me, please? | Pouvez-vous m’aider s’il vous plaît ? / Pourriez-vous m’aider s’il vous plaît ? (formal) or Peux-tu m’aider s’il te plaît ? / Pourrais-tu m’aider s’il te plaît (informal) | [puve vu mɛːde sɪl vu plɛ] | [puve vu mede sil vu plɛ] |
| Where are the toilets? | Où sont les toilettes ? | [u sõ le twalɛt] | [u sõ le twalɛt] |
| Do you speak English? | Parlez-vous (l')anglais ? / Est-ce que vous parlez (l')anglais ? | [ɛs kœ vu paʁle lãɡlɛ] | [paʁle vu ɒ̃ɡlɛ] |
| I do not speak French. | Je ne parle pas français. | [ʒœ nœ paʁl pɔ fʁãsɛ] | [ʒø nø paʁl pa fʁɒ̃sɛ] |
| I do not know. | Je sais pas. (syntax mistake and over-familiar) Je ne sais pas. Je ne sais. (formal, rare) | [ʒœ se pɔ] [ʒœ n(œ) se pɔ] [ʒœ n(œ) se] | [ʒø sɛ pa] [ʒø n(ø) sɛ pa] [ʒø n(ø) sɛ] |
| I know. | Je sais. | [ʒœ se] | [ʒø sɛ] |
| I am thirsty. | J’ai soif. (literally, "I have thirst") | [ʒe swaf] | [ʒe swaf] |
| I am hungry. | J’ai faim. (literally, "I have hunger") | [ʒe fẽ] | [ʒɛ fæ̃] |
| How are you? / How are things going? / How is everything? | Comment allez-vous ? (formal) or Ça va ? / Comment ça va ? (informal) | [kɔmã t‿ale vu] | [kɔmɒ̃ t‿ale vu] |
| I am (very) well / Things are going (very) well // Everything is (very) well | Je vais (très) bien (formal) or Ça va (très) bien. / Tout va (très) bien (informal) | [ʒœ vɛ (tʁɛ) bjẽ] | [ʒø vɛ (tʁɛ) bjæ̃] |
| I am (very) bad / Things are (very) bad / Everything is (very) bad | Je vais (très) mal (formal) or Ça va (très) mal / Tout va (très) mal (informal) | [ʒœ vɛ (tʁɛ) mal] | [ʒø vɛ (tʁɛ) mal] |
| I am all right/so-so / Everything is all right/so-so | Assez bien or Ça va comme ci, comme ça or simply Ça va.. (Sometimes said: « Couci, couça. », informal: "bof") i.e. « Comme ci, comme ça. ») | [ase bjẽ] | [ase bjæ̃] |
| I am fine. | Ça va bien. | [sa vɔ bjẽ] | [sa va bjæ̃] |
| (How) may I help you? / Do you need help? / | (Comment) puis-je vous aider ? Avez-vous besoin d'aide ? | [(kɔmã) pɥiʒ vu z‿ɛːde] | [(kɔmɑ̃) pɥiʒ vu z‿ede] |